PYTHON
At Mytegen, we offer a thorough and practical approach to mastering Artificial Intelligence, ensuring you acquire the skills essential for thriving in the tech industry.
By enrolling in our Artificial Intelligence course, you’ll gain hands-on experience, up-to-date knowledge, and the confidence to build fully functional web applications from the ground up.
Duration
30 Days

Mode of Training
Inclass & Online
Projects
3

Assessments
Topic Wise
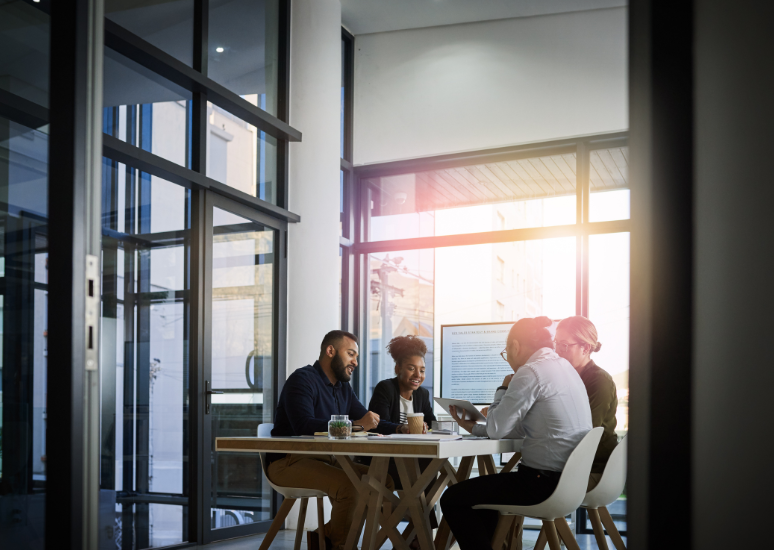

WHY PYTHON?
C Programming Course is the cornerstone of modern computing. With its unmatched speed and efficiency, C is the language of choice for everything from operating systems to embedded systems and game development. It’s not just a language; it’s a gateway to understanding how computers work at the most fundamental level.
- Solidify Your Foundations
- Boost Performance
- Versatile Applications
- Career Advancement
PYTHON COURSE OVERVIEW
Dive into the world of C Programming Mastery and emerge as a skilled programmer ready to tackle real-world challenges. This course combines interactive learning with hands-on experience, providing you with a thorough understanding of C programming.

Interactive Labs
Get hands-on experience with coding exercises and projects.

Real-World Applications
Build practical projects that reflect industry needs.

Expert Instructors
Learn from seasoned professionals with years of industry experience.

Comprehensive Resources
Access exclusive study materials, cheat sheets, and coding resources.

KEY HIGHLIGHTS
Embark on a journey to master C programming through a course designed for both beginners and those looking to refine their skills. This program provides a perfect blend of theory and practice, ensuring you gain not only knowledge but also hands-on experience. Guided by industry experts, you’ll navigate from fundamental concepts to advanced programming techniques. By the end of the course, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle complex coding challenges with confidence.
- Comprehensive Curriculum: Covers everything from basic syntax to advanced topics like pointers and memory management.
- Hands-On Projects: Apply what you learn through real-world coding exercises and projects.
- Expert Instructors: Learn from professionals with extensive experience in the industry.
- Flexible Learning: Access course materials and sessions according to your schedule.
- Certification: Earn a recognized certification upon course completion to enhance your career prospects.
WHO CAN PURSUE PYTHON
Absolute Beginners
Ideal for those with no coding background, offering a strong foundation in programming.

Students
Perfect for computer science and engineering students aiming to solidify their understanding of core programming concepts.
Industry Professionals
A valuable skill for software developers, engineers, and IT specialists looking to enhance their expertise.

Tech Enthusiasts
Great for hobbyists who want to dive deeper into the workings of software and systems.

Career Switchers
An excellent starting point for those transitioning into the tech industry, providing essential coding knowledge.
SKILLS COVERED
Acquire essential programming skills and more
TOOLS AND TECHNOLOGIES





JOB ROLES

Python Developer
Proficiency in Python, understanding of frameworks like Django or Flask, knowledge of databases

Automation Engineer
Creating and maintaining automated scripts to streamline repetitive tasks, improve efficiency

DevOps Engineer
Working on the integration and deployment of applications. Automating the infrastructure setup

Cybersecurity Analyst
Identifying and mitigating security vulnerabilities within systems and applications

Application Developer
Create and optimize applications that run on various platforms, including desktop

Game Developer
Creating games using Python, typically with game development frameworks such as Pygame

Cloud Engineer
Developing, deploying, and managing cloud-based applications and services.

Quantitative Analyst
Using Python to model financial markets, analyze risk, and develop trading.

Web Developer
Building and maintaining the server-side logic of web applications.
- Program
- Programming
- Programming Languages
- Types of software
- Data Types
- Variables
- Control Structures
- Functions
- Lists and Dictionaries
- Object-Oriented Programming
- Modules and Packages
- File I/O
- constants
- Data Types
- Type Qualifiers
- How does the data stored in Computers Memory
- Variables
- Variable Declaration
- Variable Assignment
- Variable Initialization
- Comments
Defining Constants
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Membership Operators
- Identity Operators
- Ternary Conditional Operator
- Expressions
- Input-Output Library Functions
- Non-formatted Input and Output
- Character oriented Library functions
- Compiler, Linker and Loader
- Program execution phases
- Formatted Library Functions
- Mathematical Library Functions
- Structure of a C Program
- IDE
Basic programs
- Conditional Control Statements
- if
- if-else
- nested if-else
- if-else-if ladder
- Multiple Branching Control Structure
- switch-case
- Loop Control statements
- while
- do-while
- for
- Nested Loops
- Jump Control structures
- break
- continue
- goto
- return
- Programs
- Arrays
- One dimensional arrays
- Declaration of 1D arrays
- Initialization of 1D arrays
- Accessing element of 1D arrays
- Reading and displaying elements
- Programs on 1D Arrays
- Two dimensional arrays
- Declaration of 2D arrays
- Initialization of 2D arrays
- Accessing element of 2D arrays
- Reading and displaying elements
- Programs on 2D Arrays
- Three dimensional arrays
- String Concept
- Introduction to String in C
- Storing Strings
- The string Delimiter
- String Literals (String Constants)
- Strings and Characters
- Declaring Strings
- Initializing Strings
- Strings and the Assignment Operator
- String Input Functions / Reading Strings
- String Output Functions / Writing Strings
- String Input-Output using fscanf() and fprintf() Functions
- Single Character Library Functions / Character Manipulation in the String
- String Manipulation Library Functions
- Programs Using Character Arrays
- Array of Strings (2D Character Arrays)
- Programs Using Array of Strings
- Understanding Memory Addresses
- Pointer Operators
- Pointer
- Pointer Advantages and Disadvantages
- Declaration of Pointer Variables
- Initialization of Pointer Variables
- Dereferencing / Redirecting Pointer Variables
- Declaration versus Redirection
- Void Pointer
- Null Pointer
- Compatibility
- Array of Pointers
- Pointer to Pointer
- Pointer Arithmetic
Dynamic Memory Allocation Functions
- Functions
- Advantages of using functions
- Defining a function
- Calling a function
- Return statement
- Function Prototype
- Basic Function Designs
- Programs Using Functions
- Scope
- Recursion
- Iteration vs Recursion
- Nested functions
- Variable Length Number of Arguments
- Parameter Passing Techniques – Call by value & Call by Address
- Functions Returning Pointers
- Pointers and One-Dimensional Arrays
- Pointers and Two-Dimensional Arrays
- Passing 1D arrays to Functions
- Passing 2D arrays to Functions
- Pointers and Strings
- Passing Strings to Functions
- Pointer to Function
- Object Attributes
- Scope
- Extent
- Linkage
- auto
- static
- extern
- register
- The #include Preprocessor Directive & User defined header files
- The #define Preprocessor Directive: Symbolic Constants
- The #define Preprocessor Directive: Macros
- Conditional Compilation Directives
- #if
- #else
- #elif
- #endif
- #ifdef
- #ifndef
- #undef
- #error
- #line
- #pragma
- Structures
- Structure Type Declaration
- Structure Variable Declaration
- Initialization of Structure
- Accessing the members of a structure
- Programs Using Structures
- Operations on Structures (Copying and Comparing Structures)
- Nested structures (Complex Structures)
- Structures Containing Arrays (Complex Structures)
- Array of Structures (Complex Structures)
- Pointer to Structure
- Accessing structure member through pointer using dynamic memory allocation
- Pointers within Structures
- Self-referential structures
- Passing Structures to Functions
- Functions returning Structures
- Unions
- Differences between Structures & Unions
- Enumerated Types / enum keyword
- The Type Definition / typedef keyword
Bit fields
WHY MYTEGEN ?
MYTEGEN stands out as your premier choice for tech education
Up-to-Date Curriculum
Benefit from the latest and most relevant course material.
Industry Experts
Learn from seasoned professionals with hands-on experience.
Practical Experience
Gain valuable skills through interactive exercises and real-world projects.
Personalized Support
Enjoy tailored guidance and mentorship to help you succeed.

HOW WE DIFFER FROM OTHER ?
Cutting-Edge Curriculum
Dive into a curriculum that evolves with industry trends, preparing you for today’s challenges.
Elite Trainers
Learn from industry leaders who bring real-world expertise and practical insights to every lesson.
Engaged Learning
Experience immersive, hands-on coding exercises and projects that mirror real-world scenarios.

Tailored Support
Receive personalized guidance and continuous feedback to ensure your success and growth.
Advanced Teaching Techniques
Benefit from innovative methods and tools designed to enhance your learning experience.
Career Enhancement
Access dedicated career services, including job placement support and professional development resources.
Get In Touch With Us
Removed demands expense account in outward tedious do. Particular way thoroughly.
Office Phone Number
+91-8977799052
Company Office Address
Metro Pillar: 1545, Sirisha Mess Entrance, Dilsukhnagar, Hyderabad, Telangana
Office Email Address
contactusmytegen@gmail.com
Write Us
FAQ
Frequency Asked Question
Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its readability and versatility. It is commonly used in web development, data science, AI, and automation.
Python is a simple, readable, dynamically-typed language that supports multiple paradigms and has a vast standard library.
Python does not have explicit pointers, but it handles memory management automatically through references to objects, making pointer manipulation unnecessary.
Python is a high-level, interpreted, dynamically-typed language with built-in garbage collection, while C is a low-level, compiled, statically-typed language that requires manual memory management.
Our courses offer a cutting-edge curriculum, taught by industry experts, and feature hands-on projects that provide practical, real-world experience.
Our instructors are seasoned professionals with extensive industry experience, providing insights and practical skills that are directly relevant to the field.
Students benefit from personalized mentorship, detailed feedback, and comprehensive support throughout their learning journey at MYTEGEN.

